slap tear clinical tests|shoulder labral tear special tests : consultant SLAP tear type is determined by the anatomical location of the tear as well as the severity of its extension. A paralabral cyst found on MRI is a diagnostic clue for a SLAP tear. .
Fotos. Foto Quadros. Foto Presentes. Canecas. Calendários. Tok Pop. Promoções. X. Poxa, essa promoção expirou.
{plog:ftitle_list}
webfutexcel.com.br. a) Para determinar a posição de cada clube na Fase de Grupos. clique e mova-os para cima e para baixo. b) Para avançar clique abaixo em: Fase Eliminatória. Simulador da Libertadores. Simule a classificação de todas as fases da Libertadores.
A SLAP lesion (Superior Labrum from Anterior to Posterior tear) generally occurs as result of overuse injury to the shoulder in overhead athletes or traumatic falls in older patients and can result in deep shoulder pain and .
No single orthopedic maneuver reliably predicts a SLAP tear. However, research is filled with over two dozen tests to help establish this diagnosis. In this week’s blog, we’ll dive deeper into three of the most useful . Superior labral anterior to posterior (SLAP) lesions constitute a recognized clinical subset of complex shoulder pain pathologies. SLAP lesions demonstrate a predilection for .A SLAP tear is an injury to the labrum of the shoulder, which is the ring of cartilage that surrounds the socket of the shoulder joint. Injuries to the superior labrum can be caused by acute trauma or by repetitive shoulder motion.
The purpose of this paper is to review the pathomechanics, diagnosis, and treatment of SLAP lesions. We will specifically review some of the physical examination tests that are used to diagnose SLAP lesions and report .
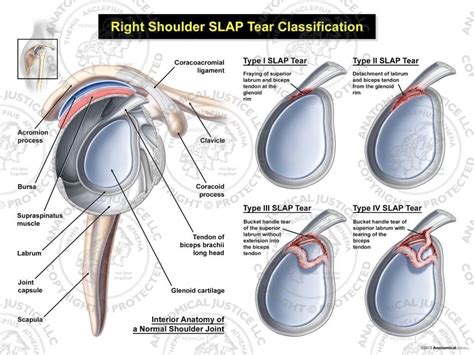
SLAP tear type is determined by the anatomical location of the tear as well as the severity of its extension. A paralabral cyst found on MRI is a diagnostic clue for a SLAP tear. . The pathophysiology, clinical presentation, diagnosis, and nonsurgical management of SLAP tears are reviewed here. The general approach to patients with . The acronym “SLAP” stands for Superior Labrum Anterior Posterior, and is used to describe a tear or detachment of the shoulder’s superior glenoid labrum; generally originating .
Biceps load test II: a clinical test for SLAP lesions of the shoulder. Arthroscopy 2001 February; 17(2):160-164. ↑ 2.0 2.1 Somerville L, Willits K, Johnson A, Litchfield R, LeBel ME, Moro J, et al. Clinical Assessment of Physical .Introduction [edit | edit source]. Traditionally Orthopaedic Special tests were used to assist in the diagnostic process by implicating specific tissue structures that are either dysfunctional, pathological, or lack structural integrity, confirming the .
These tears are common in overhead throwing athletes and laborers involved in overhead activities. The pathophysiology, clinical presentation, diagnosis, and nonsurgical management of SLAP tears are reviewed here. The general approach to patients with shoulder pain, the shoulder examination, and rotator cuff injuries are discussed separately.
The O’Brien test can help diagnose a tear in the top or superior part of your labrum. A superior labrum tear is also called a SLAP tear, which stands for superior labrum, anterior to posterior. The O’Brien test can also rule out other problems, such as: Rotator cuff tear. Shoulder impingement syndrome.A SLAP tear is an injury to the labrum of the shoulder, which is the ring of cartilage that surrounds the socket of the shoulder joint. Injuries to the superior labrum can be caused by acute trauma or by repetitive shoulder motion. . Perform specific tests by placing your arm in different positions to reproduce your symptoms. Maybe examine . These tears are common in overhead throwing athletes and laborers involved in overhead activities. The pathophysiology, clinical presentation, diagnosis, and nonsurgical management of SLAP tears are reviewed here. The general approach to patients with shoulder pain, the shoulder examination, and rotator cuff injuries are discussed separately. The evidence to support the use of clinical tests for superior labral anterior to posterior complex (SLAP) is weak or absent. The purpose of this study is to determine the diagnostic validity of physical examination maneuvers for SLAP lesions by performing a methodologically rigorous, clinically applicable study. . (SLAP tear present = 1.8 .
Background: The clinical diagnosis of a superior labral anterior posterior (SLAP) tear is extremely challenging. Most studies that advocate selected tests have errors in study design or significant bias, or both. The purpose of this study was to identify the diagnostic utility of the Active Compression/O'Brien's test, Biceps Load II test, Dynamic Labral Shear test (O'Driscoll's .
types of slap tears
Kim SH, Ha KI, Ahn JH, Kim SH, Choi HJ. Biceps load test II: A clinical test for SLAP lesions of the shoulder. Arthroscopy 2001;17:160-164. 44: 103: 5.4: 29: Conway JE. Arthroscopic repair of partial-thickness rotator cuff tears and SLAP lesions in professional baseball players. . SLAP tears were first described by Andrews et al. 1 in 1985 .
Synopsis Superior labral tears (SLAP lesions) can pose a significant challenge to orthopaedic surgeons and rehabilitation specialists alike. Although advancement in arthroscopic techniques has enhanced arthroscopic repair of SLAP lesions, the clinical diagnosis of SLAP lesions can still be difficult. There is a variety of etiologic factors associated with SLAP lesions .In 2012, Cook et al. investigated the diagnostic accuracy of five orthopedic clinical tests for the diagnosis of SLAP lesions among which they included the labral tension test. In patients where an isolated SLAP lesion was the suspected scenario, the test yielded a sensitivity of 40% and specificity of 75% and thus lacking the capacity to .The best tests available to make the diagnosis of a labral tear are magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) scans or a test called a CT-arthrogram (the latter is a CAT scan preceded by an arthrogram where dye is injected into the shoulder). Both of these tests are relatively good at defining a labrum tear due to a subluxation or dislocation, but they .
Background and purpose: The Magnetic Resonance Arthrogram (MRA) has served as the gold standard for identifying patients with possible Superior Labrum Anterior-Posterior (SLAP) lesions and are often required by orthopaedic surgeons prior to clinical evaluation. However, as the literature shows MRA sensitivity as 0.65-0.98, and specificity between 0.80-1.00, there is still .
Posterior labrum tear: This tear occurs at the back of the shoulder joint. SLAP tear: A superior labrum anterior to posterior (SLAP) tear occurs at the top of the glenoid (shoulder socket) and extends from the front to the back, where the biceps tendon connects to the shoulder. This is a common injury for athletes such as baseball pitchers and . What is a SLAP tear? SLAP stands for "superior labrum from anterior to posterior." This type of shoulder labral tear occurs at the top (“superior”) of the glenoid labrum where it connects to the biceps tendon, and . Get detailed information about labral tears, including SLAP tears and Bankart tears, shoulder labral tear symptoms, diagnostic tests, and treatment, including surgery. Menu. Find a Doctor. Back. . right hospital and . External rotation is applied until the patient becomes apprehensive. At that point, the patient is asked to contract the biceps muscle. If the patient’s pain or apprehension decreases, the test result is negative for .
Stetson WB, Templin K. The crank test, the O’Brien test, and routine magnetic resonance imaging scans in the diagnosis of labral tears. Am J Sports Med. 2002;30:806–809. Yang-Soo Kim, Jung-Man Ha, Kee Yong, et al. The passive compression test: A new clinical test for superior labral tears of the shoulder. Am J Sports Med, 2007;35(9):1489-94.“A new SLAP test: the supine flexion resistance test.” Arthroscopy: The Journal of Arthroscopic Related Surgery: Official Publication of the Arthroscopy Association of North America and the International Arthroscopy Association 24.5 (2008): 500-5. ↑ Guanche, Carlos A, and Donald C Jones. “Clinical testing for tears of the glenoid labrum.” In this educational video we take you through what SLAP tears are using our 3D anatomy model, explore mechanisms of injury, discuss how SLAP tears are manage.
SLAP Lesion Cluster 1 | Shoulder Assessment. According to a study done by Schlechter et al. (2009), a combination of the Active Compression Test and the Passive Distraction test yields a positive likelihood ratio of 7.0 for 2 positive tests and a negative likelihood ratio of 0.33 for two negative tests. This test cluster therefore has moderate clinical value to confirm or rule out .To test for the presence of a subscapularis tendon tear, first have the patient to bring the hand on the back at the level of the lumbar region. Then, passively separate the hand from the back until full internal rotation of the shoulder is achieved. At this point ask the patient to actively keep the hand away from the back.Some of the tests were more accurate with younger patients. But there wasn’t one individual test that could diagnose a type II SLAP lesion. In other words, it wasn’t possible with any of these clinical tests to tell when the biceps anchor was detached. Results of combining tests weren’t any different between the two age groups.Rosas et al. (2017) have conducted a literature review and have come up with a test cluster. They found that the uppercut test combined with tenderness to palpation of the long head of the biceps had the highest accuracy to diagnose pathology of the proximal biceps with a sensitivity of 88.3% and a specificity of 93.3%. Although accuracy seems to be high, this combination has not been .
The results indicate that a combination of at least three positive SLAP lesion tests may be clinically useful in diagnosing a shoulder SLAPLesion with greater diagnostic accuracy than those reported for MRI/MRA, thus improving patient management by referring only those who may require surgical intervention to a physician. Background and Purpose The Magnetic . The incidence and aetiology of SLAP lesions remain uncertain. Snyder et al 5 evaluated 2375 shoulder arthroscopies, and 140 (6%) of them revealed a SLAP lesion. Maffet et al 3 reported that 84 (12%) of 712 patients examined arthroscopically had a SLAP lesion, and Handelberg et al 6 reported that 32 (6%) of 530 patients had such a lesion. One review of the .The clunk test is often performed during the shoulder clinical exam to diagnosis a SLAP tear. Remember, SLAPs can occur for various reasons, but a Clunk Tes.
slap tear special test
webExplore Oasis's discography including top tracks, albums, and reviews. Learn all about Oasis on AllMusic.
slap tear clinical tests|shoulder labral tear special tests